Computer vision (CV) is an artificial intelligence (AI) field that enables systems to derive meaningful information from digital images and videos. Globally, the computer vision market is expected to reach $41 billion by 2030, with retail AI alone expected to reach nearly $15 billion within the next few years.
Although opportunities for using CV and AI in retail abound would-be innovators must also face problems and points of failure. Companies approach us all the time for help with a litany of data preparation challenges that occur along the AI development lifecycle. For example, some companies contend with scaling data annotation volume and increasing the quality of their training data. Others need help choosing the right annotation tools. Some companies struggle with adapting capacity based on seasonality and new product launches; others need help adjusting to changes in business requirements, use cases, and even labeling tasks and techniques.
To dominate—or even keep pace—in this explosive industry, forward-thinking companies plan how to get the work done while focusing on their core mission to improve customer and employee experiences, develop innovative products, and generate ROI.

Read the full guide below, or download a PDF version of the guide you can reference later.
This guide dives into the wave of computer vision and AI robotics innovation in the retail industry. As you read, you’ll learn about:
- Emerging in-store machine vision robotics use cases and retail automation technologies.
- Technologies for modernizing warehouse and logistics operations.
- Computer vision in last-mile delivery—the next wave of retail AI
- How to make computer vision for retail AI happen in your organization
We’ll also share a list of additional resources you may find helpful and an introduction to CloudFactory, which provides the people-power needed for large-scale computer vision data labeling and data annotation projects.
Introduction:
Will this guide be helpful to me?
This guide is for you if you’re:
- Learning how AI, robotics, and automation can improve retail operations and the retail experience.
- Building computer vision models and need to scale data annotation teams and accelerate data labeling pipelines while maintaining data quality.
- Learning about different data annotation tools and data labeling workforce options.
- Trying to maximize your use of an expertly managed human-in-the-loop (HITL) workforce.
Retail Computer Vision Use Cases
Computer Vision in The Warehouse:
Technology for Warehouse Operations and Retail Logistics
For all retailers—brick-and-mortar and ecommerce operations—smooth warehouse and logistics operations are the magic behind seamless shopping experiences. Most consumers don’t understand everything Amazon does to get packages to our door, sometimes within hours. We simply delight in the experience and, at this point, expect it without fail.
Yet on the backend, retailers like Amazon must fight the good fight against global supply chain logjams, labor shortages, skyrocketing costs, and even issues with worker safety, inventory control, and space optimization.
Computer vision automation and robotics change the game by taking on the precise, routine, dangerous, and downright dull jobs to be done: Receiving, storing, picking, packaging, shipping, and tracking inventory. Powered by computer vision, autonomous mobile robots find and move items where they need to be; drones identify products for inventory control; and robotic arms recognize, lift, and move and sort products. It’s a beautiful symphony of robots operating alongside humans and continuing long after people have gone home for a well-deserved night’s rest. Sakichi Toyoda would marvel at the efficiency.
And lest you pause, thinking that these technologies are still in their infancy, consider the latest market research study by Research and Markets. This study says that the autonomous mobile robots (AMR) and automated guided vehicles (AGV) market will reach $13.2 billion by 2026, with a 35% growth rate. Both AGVs and AMRs collectively will cross the installed base of 1.5 million in the next five years. Five years! Mobile robots will soon be the new standard—common tools helping you with your everyday, operational activities.
Let’s look at a few of these exciting new technologies.
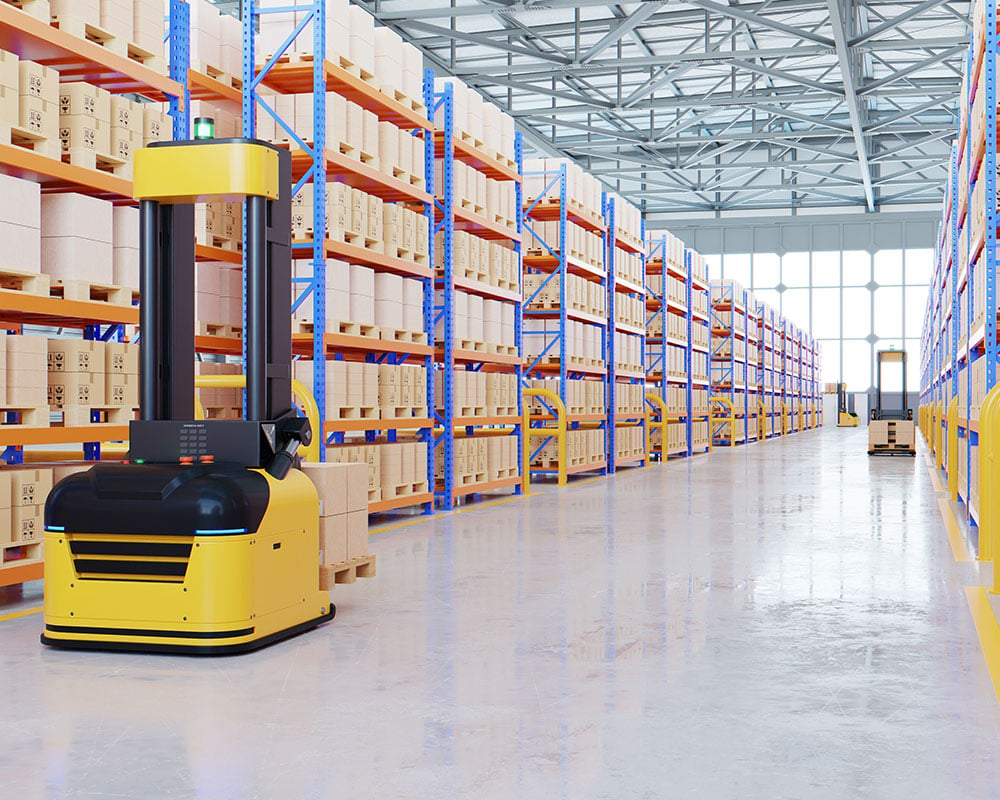

Autonomous Mobile Robots
Autonomous mobile robots can perform many warehouse tasks when armed with machine vision. They can increase worker safety and productivity by reaching for hard-to-get or heavy items. They can handle inventory control and transport goods from point to point. They can also pick, sort, and pack items for delivery. Is there anything AMRs can’t do these days?
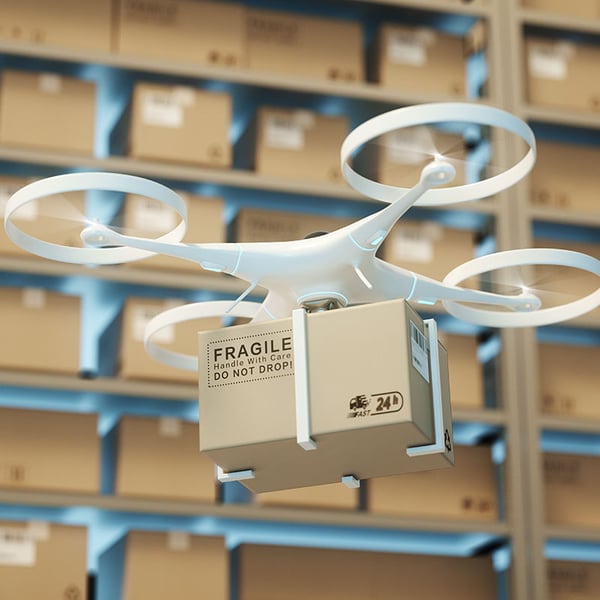

Drones
Inventory control is the most common use case for CV-enabled drones in retail warehouses. With their ability to hover and fly autonomously, drones can safely access all areas of warehouses to audit inventories and locate specific pallets or products. Retailers also use drones for inventory management, increasing the speed and accuracy of an otherwise labor-intensive task of manual inventory counting. Drones can cover some serious ground without bumping into things, and they stay out of the way of nearly all on-the-ground operations.
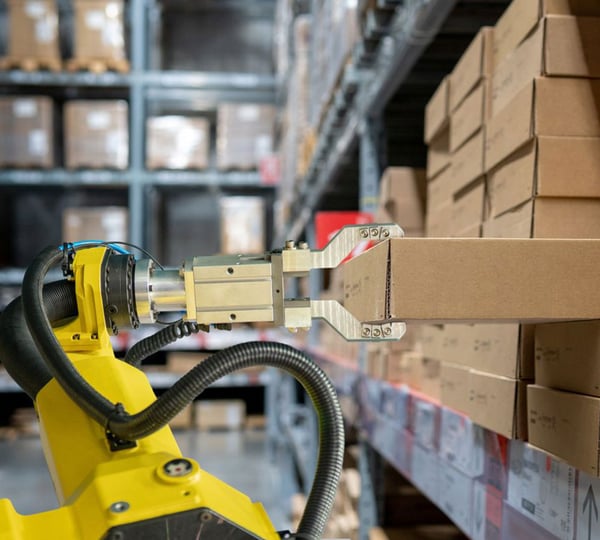

Robotic Arms
Warehouses have been using robotic arms for decades to lift heavy items, access hard-to-reach items, and package products for delivery. Now, a combination of cameras, grippers, and artificial intelligence help pick and pack robots work more independently with limited intervention from human operators. This helps improve warehouse operations by reducing labor costs, diverting short-staffed teams to critical tasks, and accelerating fulfillment.
Companies to watch for in operations and logistics
- Dexterity provides robotic solutions for logistics, warehousing, and supply chain operations.
- Boston Dynamics provides flexible warehouse robotics to improve worker safety and increase productivity throughout the warehouse.
- Fetch Robotics deploys safe, reliable, and versatile AMRs in the warehousing and intralogistics markets.
- Locus Robotics designs and builds innovative autonomous mobile robots that work collaboratively alongside workers in the logistics and fulfillment industries.
- Symbotic has developed proprietary and innovative robotics and software to deliver an advanced automation solution to make the supply chain faster, more efficient, and more profitable for manufacturers, distributors, and retailers of all sizes.
Computer Vision in The Store:
Use Cases for Machine Vision Robotics and Automation in Retail
Like kids in a candy store, your shoppers are clamoring for frictionless experiences. And though you want to oblige, you must first deal with staff shortages, global supply chain issues, and the ecommerce takeover.
The good news is that machine vision robotics and automation offer relief. Retailers today are using automation to dramatically improve the in-store experience, which is not just better for shoppers; it’s also huge for employees and a store’s bottom line.
Depending on where you live, you may have already noticed robots roaming the aisles of your favorite stores. What are they doing? What value do they deliver? Let’s look inside.
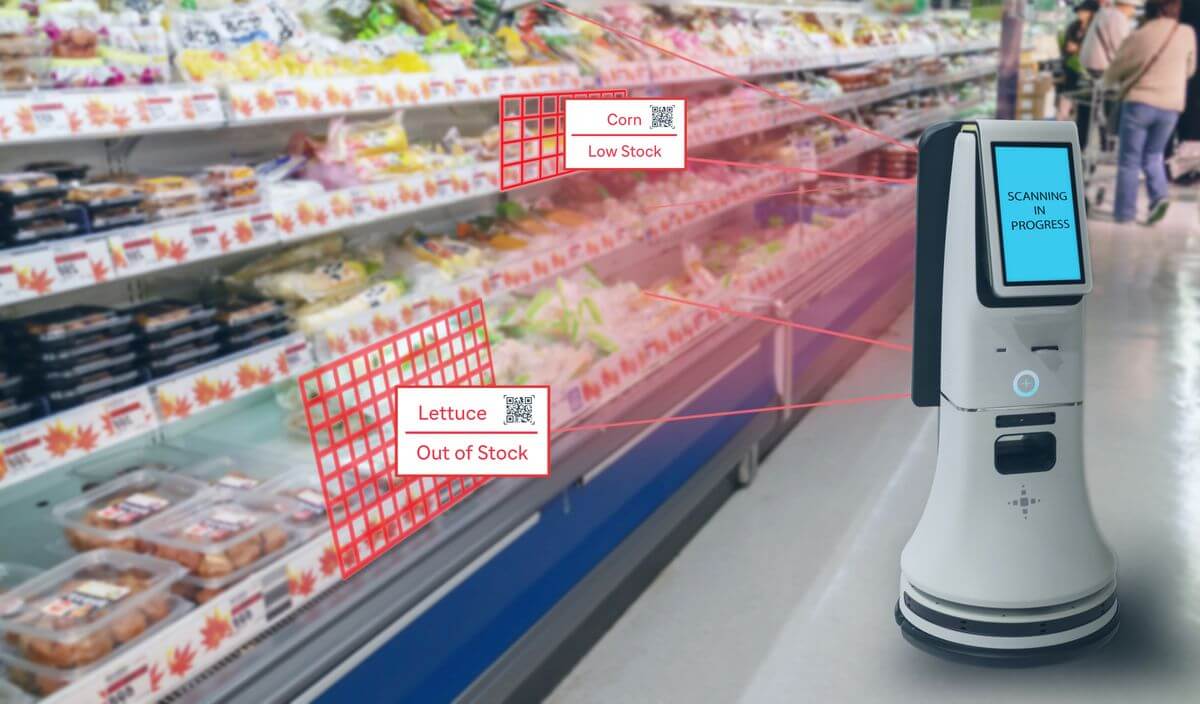

Inventory Monitoring
Some retailers use robots to scan store shelves and track inventory levels. Robots can flag store associates when items run low so that either an associate or a robot can restock quickly. On-demand restocking does triple duty:
- Customers don’t have to interact with staff to ask if there’s more milk in the back, which is good because research tells us that customers generally don’t like to interact! One study found that 73% of shoppers prefer to use in-store self-service than engage with store employees.
- Store associates don’t have to wander the aisles looking for products to stock.
- Stores never lose sales on items like milk because it’s always on display and available for purchase.
The same robots can also alert associates when shoppers or other associates misplace items, which leads to better customer experiences. Have you ever felt the swell of frustration when a price rings up wrong? You have to stand there, helpless, waiting for the associate to check the price while the shoppers behind you glare and tap their feet. When the associate finally returns, they tell you the too-high cost is correct. “Sorry,” they say. “The item was misplaced.” With suitable robots, those experiences will be a thing of the past. More advanced robots can even tell you when produce items have expired so you can pull and replace them with fresh goods. Another in-store experience won, thanks to computer vision and retail AI.
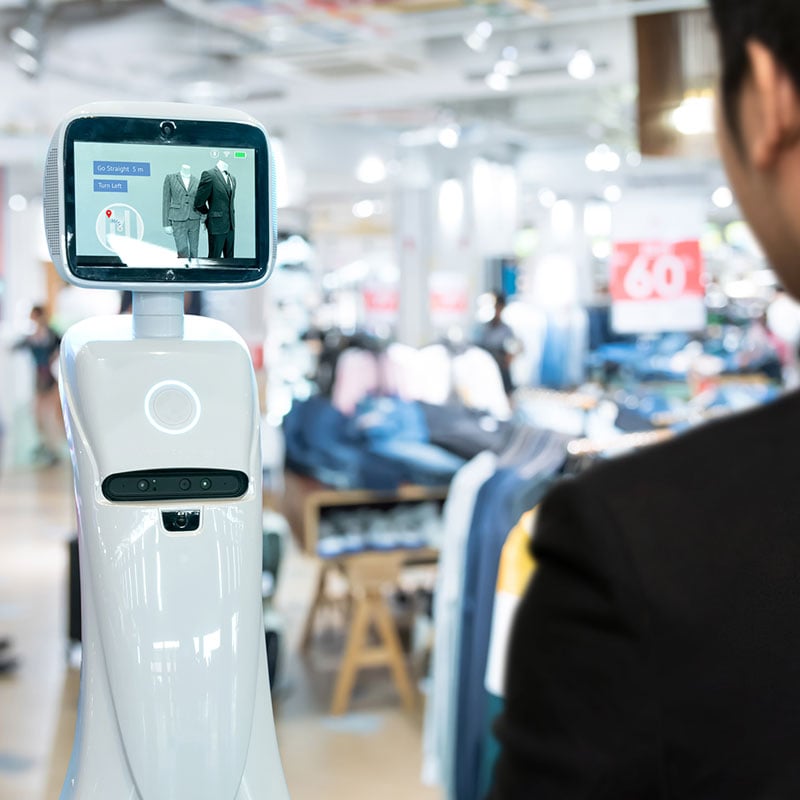

Shopper Assistance
Have you ever interacted with a roaming kiosk that helps you find a particular item? You either type the item’s name into the robotic kiosk or tell it what you want, and it directs you to the items’ exact location. When an item is out of reach—too high, too low—the same CV-enabled robot friend gets it off the shelf and places it in your cart. Since 2016, Lowe’s Home Improvement’s Lowebot has been helping shoppers while also scouting for and replenishing low inventory and making sense of consumer traffic patterns.

Cleaning Machines
It’s late. All shoppers and store associates are home watching Hulu and Netflix. Back at the store, robots work through the wee hours of the morning, tirelessly cleaning the floors until they shine. Unlike automated home vacuum robots, which follow a predefined pattern, robots using trained computer vision models hit every nook and cranny. They learn your store’s floor instead of being limited by programmed paths. And when something spills, breaks, or otherwise threatens human safety, these same robots can identify the source of the incident, block off potentially dangerous areas, and clean up the mess. “C-3PO, clean up on aisle 3, calling C-3P0.” Except for your robots, no loudspeaker announcement is required.

Unloading and Sorting Deliveries
Muscle strains and sprains are the most common on-the-job injuries for retail employees. From the moment a delivery truck arrives at your store, computer vision-powered robotics—including articulated robot arms, autonomous guided carts, and unit load and heavy burden carriers—reduce incidences of common injuries by unloading and sorting items in the back of the store. Accenture surveyed supply chain leaders and found that although warehouse workers are receptive to the benefits of robots, they also want more training to succeed with the new technologies.

Loss Prevention
Another emerging use case using computer vision-enabled robots for anti-theft and loss prevention. Robots roam the store, in tandem with or separate from a fixed network of cameras and sensors, to ensure shoppers pay for the items they take from the shelves. These robots also alert retail store associates to suspicious activity—an ingenious complement to autonomous checkout systems.

Autonomous Checkout
The most recognizable use of computer vision in retail is the autonomous checkout system, also known as frictionless checkout, cashierless checkout, smart carts, touchless retail, and seamless checkout. Autonomous checkout systems allow shoppers to pay for items without waiting in lines and with little to no assistance from cashiers. Autonomous checkouts dramatically improve the shopping experience, but high-quality data is necessary. If you’re interested in autonomous checkout, you might find this blog post helpful—Annotation Speed + Quality: 3 Workforce Approaches for Autonomous Checkout. It covers several approaches for implementing data annotation for autonomous checkout systems.
Companies to watch for in in-store robotics and automation
- Chooch computer vision applications for both brick-and-mortar retail and ecommerce include shelf space management, in-store health monitoring, and customer behavior analysis.
- Tally from Simbe Robotics is the world’s first fully autonomous shelf auditing and analytics solution.
- Berkshire Grey develops integrated AI and robotic solutions for ecommerce, retail replenishment, and logistics.
- Caper offers contactless and automated checkout powered by AI and computer vision for grocery and convenience stores.
- Veeve allows grocery retailers to provide convenient shopping experiences with the Veeve Intelligent Cart, which gives customers the freedom to skip the line and simply scan, pay, and go.
- Zippin has developed the next generation of checkout-free technology, enabling retailers to quickly deploy frictionless shopping in their stores.
- Trigo technology powers grocery stores with market-leading frictionless checkout and digitized operations.
Computer Vision in Last-Mile Delivery:
The Next Wave for Robotics and Automation in Retail
The next great wave for robotics and automation in the retail industry is using drones and other autonomous vehicles for the last mile of delivery.
Some retailers have already outsourced the last mile of delivery to third-party providers like Instacart and DoorDash, driving up costs for retailers and shoppers. Shoppers frown at the hefty delivery fees. Retailers frown at the cut providers take. You rarely read news about driver job satisfaction; people tell us it’s not fun. Fortunately for all involved, mega-retailers like Amazon have piloted drone delivery services and, in specific markets, Pizza Hut and FedEx have tested the use of autonomous vehicles for delivery.
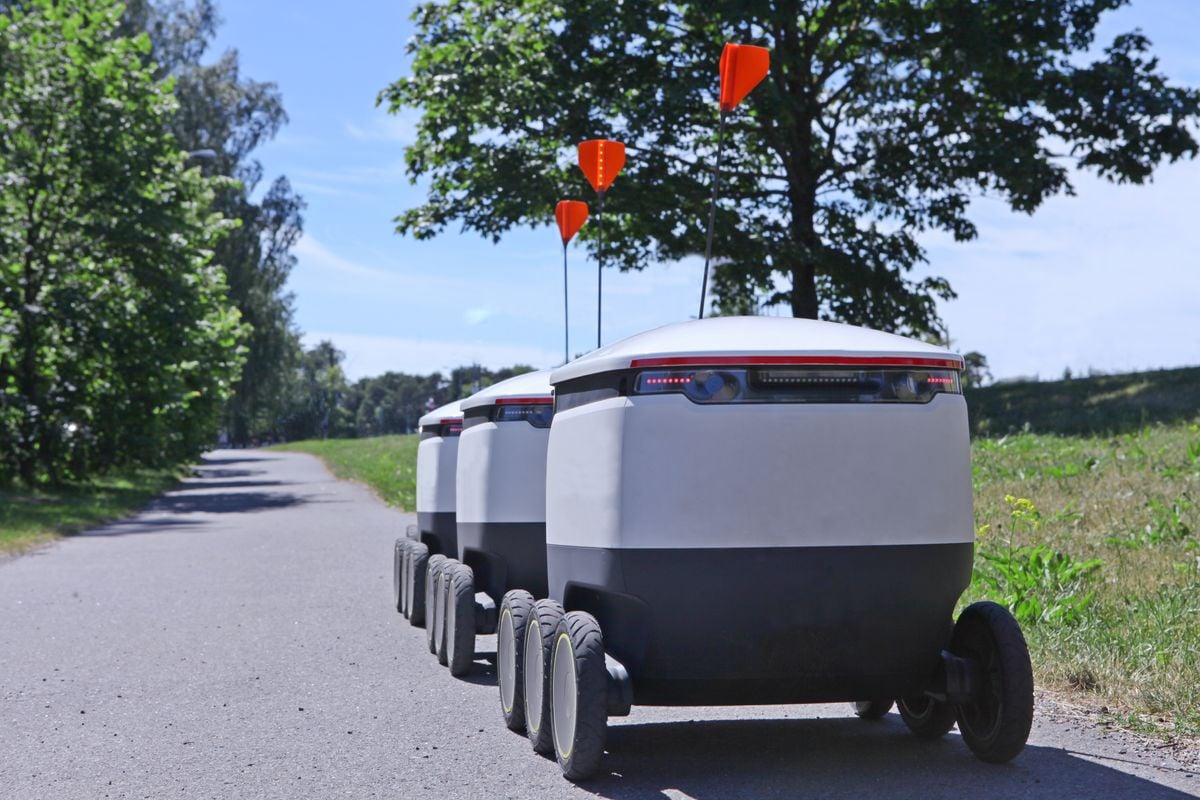

New companies are entering this market at a record pace by automating at least part of the process. For example, startups like Robomart are using computer vision to completely automate the last mile of delivery with a fleet of on-demand, mobile mini-marts that pull up right to your door so you can select the groceries you need. Keep watching this space because it won’t be long before the whole goods-creation process is automated—from production to the supply chain to our doors.
Companies to watch for in last-mile delivery automation
- Udelv is a California company that created the world's first custom-made, self-driving delivery vehicle for public roads.
- Mobileye is leading the mobility revolution with autonomous driving and driver-assist technologies, harnessing world-renowned expertise in computer vision, machine learning, mapping, and data analysis.
- Starship Technologies is building a network of autonomous delivery robots ready to serve you anytime, anywhere.
Bringing Retail AI to Life: Data Labeling Tools and Techniques
Computer Vision for Retail AI:
Making it Happen with Data Labeling and Data Annotation
Computer vision models love large quantities of quality training data, which is why making CV for retail AI a reality starts with data labeling, sometimes also called data annotation. Data annotation is the process of labeling data, so it denotes a target, which is the answer or outcome you want your machine learning model to predict. You are marking—labeling, tagging, transcribing, or processing—a dataset to give it the features you want your machine learning system to learn to recognize. Once trained, a model for retail can help improve the in-store experience, control inventory, streamline warehouse operations, and automate the checkout process.
This section covers what you need to make CV for retail AI happen, starting with an overview of the types of annotation tasks involved.
Common types of image annotation in retail AI
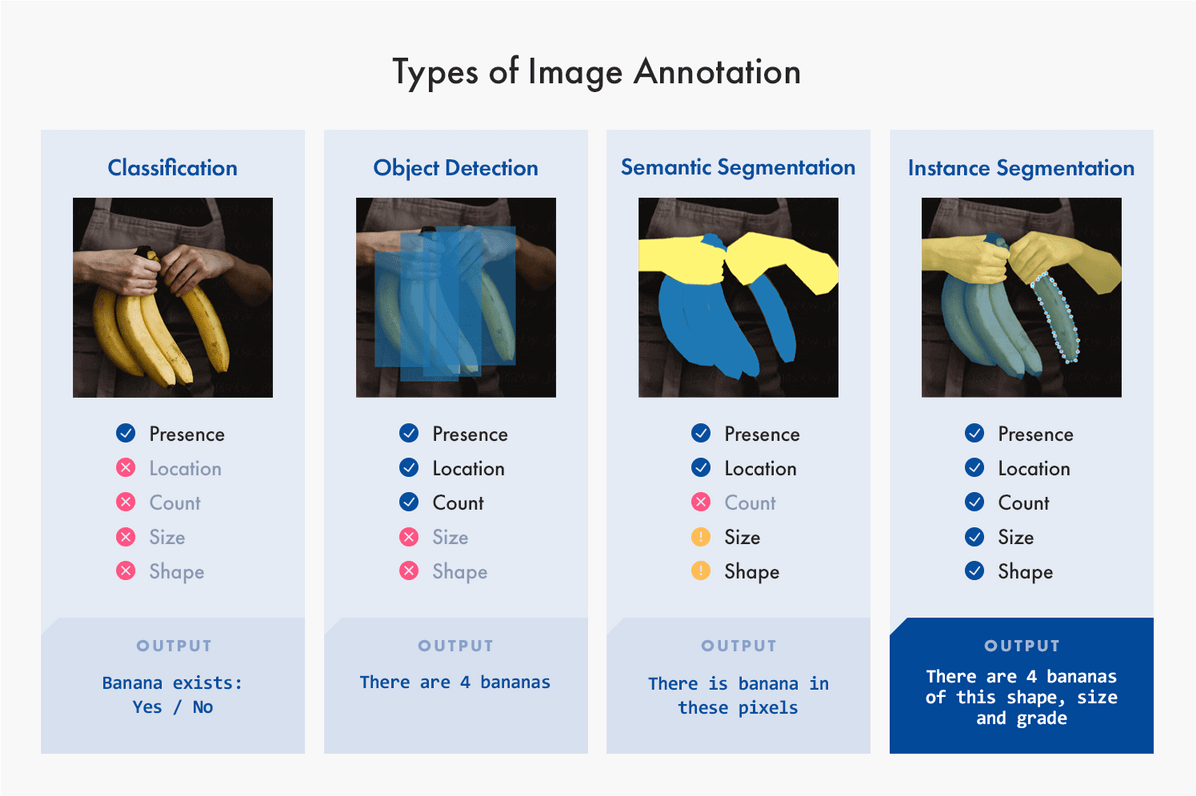
The image that follows outlines four types of image annotation: Image classification, object detection, semantic segmentation, and instance segmentation.
- In classification, labelers apply a single label to one image to train the model to recognize similar images. In the example, the labeler identifies the presence of a banana. The output is yes or no.
- In object detection, labelers identify the presence, location, and count of objects in an image by drawing boundaries around the objects. The output in our example is that there are four bananas.
- In semantic segmentation, labelers identify the presence and location of objects in an image at the pixel level by indicating the boundaries between similar objects, in this case bananas.
- In instance segmentation, labelers identify all variables—presence, location, count, size, and shape. The output of this class of segmentation is that there are four bananas of this size and shape.
The challenge for AI developers is transforming massive amounts of raw data like those images of bananas into the high-quality annotated data needed to train models.
There are two major elements of training machine learning AI models, both of which weigh heavily on the success or failure of your retail AI initiative: Data labeling tools, and the quality of the annotations by the analysts who label the data.
Let’s take a look.
Data Annotation Tooling Options
Data annotation tools can be cloud-based, on-premise, or containerized. You can use commercial tools to annotate training data pipelines for machine learning or take a do-it-yourself approach and build your own tool. Alternatively, you can choose one of the many data annotation tools available via open source or freeware.
Our web guide—Data Annotation Tools for Machine Learning—will help you understand the variables involved, from making the build or buy decision to choosing a tool if you do decide to buy. Your tooling choice matters because the right tool increases labeling productivity and yields higher-quality training data.
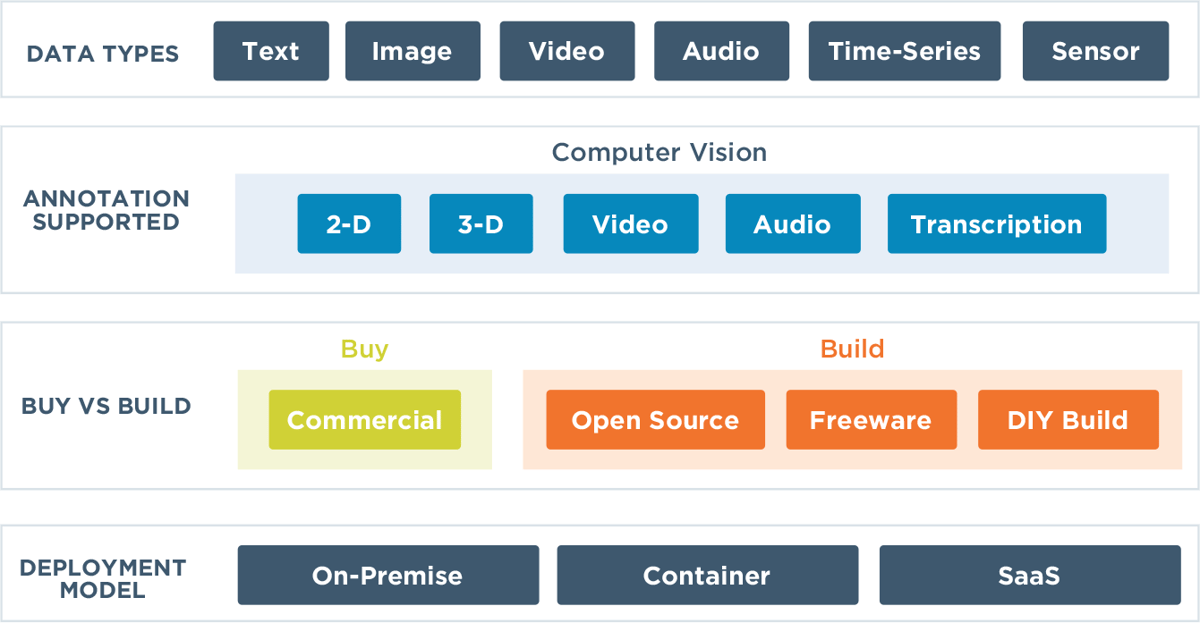
The following graphic summarizes the key elements of data annotation tools for computer vision, from data types and supported annotation to deployment models and build or buy options.
KEY ELEMENTS OF DATA ANNOTATION TOOLS
Data annotation tools are generally designed to be used with specific types of data, such as image, video, text, audio, spreadsheet, or sensor data.
They also offer different deployment models, including on-premise, container (Kubernetes), and SaaS (cloud).
Automated data annotation continues to evolve. But the industry is still at a point where ALL data annotation tools are meant to be used by humans, even tools with AI-based automated labeling capabilities. Because humans in the loop are an essential part of the process, let’s also talk about your options in that regard.
Data Annotation Workforce Options
Choosing the right people to annotate your data for retail computer vision is one of the most important decisions you’ll make. Computer vision and other machine learning models are only as good as the data they’re trained on, which means you’ll need people power, or “humans in the loop,” to prepare and quality-check your image and video annotations.
You generally have five options for your data labeling workforce:
- Employees - Employees are on your payroll, and their job descriptions may not include data annotation. Because data annotation is tedious, manual work, you may experience higher-than-usual employee turnover. Also, when you’re doing the work in-house, you’re responsible for a litany of activities beyond recruiting, hiring, and firing, including project management, workforce training, and quality management. This infographic—In-House vs. Managed Workforce—outlines the myriad tasks involved in in-house data labeling.
- Contractors - Contractors are temporary workers, either freelancers or gig workers. They may work remotely or at your location. As with employees, you shoulder the burden of recruiting, management, scaling, and training contractors.
- A managed workforce - CloudFactory is a managed workforce provider. As such, we bring you expertly managed teams of annotators with retail AI domain expertise and training on a wide range of annotation tools. With the managed workforce model, you have direct access to the analysts annotating your data, but their employer, like CloudFactory, handles vetting, training, and performance and quality management for you. If you’d like, learn more about our workforce management approach.
- Business process outsourcers (BPOs)- Business process outsourcing is the traditional outsourcing model where a third party hires workers and brings them into the office to get the work done. BPOs generally do not give you access to the people who are doing the work, nor are they likely to have access to pools of analysts with experience in retail AI.
- Crowdsourced workers - These anonymous workers are sourced using third-party platforms. Crowdsourced workers often prioritize task completion and speed over accuracy, which leads to lower-quality training data and repeat work.
Read on if you’re interested in learning more about using a managed workforce for your retail AI initiative. Next, we talk about the key variables you’ll want to consider as you explore workforce options. And then, we share how we do things at CloudFactory.
Key Elements to Look for in Your Data Labeling Workforce
Keep the following critical factors in mind as you explore your workforce options.
Quality
For your AI to be truly “intelligent,” it needs to be trained with trusted, reliable data. Look for a retail data labeling workforce with demonstrable experience and a track record of quality and customer satisfaction in the form of a high Net Promoter Score, good client references, and high-praise client testimonials and case studies. Also, confirm whether your prospective partner can meet or exceed accuracy goals and whether their QA methods match your acceptable margin of error. If you have even the slightest question of whether quality training data always comes first, pass. Some certifications, like SOCII and ISO 27001, illustrate that your prospective partner truly cares about delivering high levels of quality data annotation.
Scalability
The more scalable your workforce, the faster you’ll see results. Scale enables you to quickly expand the scope of your work, sometimes in a matter of weeks. You’ll be prepared to launch new initiatives on a dime, feed your hungry models ever-larger datasets, and generate multiple datasets at once.
Collaboration
Responsiveness is table stakes in the data labeling industry, so look for a partner who responds quickly and thoroughly to your initial outreach and questions. You should have a dedicated point of contact for your project who cascades and collects feedback, reports on progress, and manages the accuracy, speed, and agility of your project. Speed and responsiveness set the tone for your relationship and informs what the partnership might look like.
Agility
The more agile your workforce, the more machine learning initiatives they can work through as an agile workforce can quickly react to changes in task frequency, complexity, and duration. Look for a data labeling partner that can easily support changes in production models and use cases, and help you with R&D and experimentation as you develop, refine, and scale the products that grow your business.
Productivity and Tooling
In the highly competitive retail AI market, time to market is crucial to product success—and labeling speed directly correlates to the time it takes to train, tune, test, and ultimately ship a production-grade machine learning model. When considering managed workforce partners, assess their ability to accelerate time to value by asking whether they track productivity in real time, practice quality control, and offer collaboration tools—all of which CloudFactory does through our workforce management platform. Don’t know which tool to use? Let us advise you. Our expertise across many data types and use cases allows us to recommend the right tool for your current and future data annotation needs.
Capacity and Elasticity
Because demand in the retail industry always ebbs and flows, look for a flexible workforce partner able to adapt to changing capacity needs, whether known, like changes due to seasonality, or unknown, like during volume surges, or unforeseen business changes or roadblocks. If your managed workforce uses synchronous and asynchronous workflows, real-time exception handling, and static-state labeling, they’ll be ready to support you no matter which way the wind blows.
Introducing CloudFactory
CloudFactory provides a scalable, expertly trained human-in-the-loop (HITL) workforce to accelerate AI initiatives and optimize business operations. Our expert managed workforce and thoughtful approach honed over thousands of client engagements give you the flexibility, scale, and quality you need to deliver product innovations and enhance customer satisfaction.
Get quality at scale
CloudFactory consistently achieves accuracy above the acceptable margin of error benchmarks for leading computer vision developers and retail clients. We are ISO 9001 certified in quality management and offer a proven workforce model with robust quality assurance and exception handling processes to bolster the quality we deliver. We are also ISO 27001 certified in information security management. We’ve invested mightily in people, processes, and technology to protect your organization’s data.
Save time by extending your team
For one of our clients, an AI company revolutionizing shopping with autonomous checkout, we process 50K annotations each day, exceeding quality and throughput targets. CloudFactory serves as an extension of your team and scales up by rapidly learning and adapting to your business rules, objectives, and changing conditions.
Elasticity on demand
Retail tech companies rely on us to adapt to capacity and elasticity needs. When workloads shift due to seasonality, new business, and spikes in user demand, we use synchronous and asynchronous workflows and real-time exception handling with static-state labeling to stay on track for numerous retail AI clients. We also offer flexible pricing and an approach built for scale and agility.
Training computer vision solutions to perform in the real world requires a high volume of accurately labeled training data. Sure, you could toss your labeling project to an unknown crowd, an inflexible outsourcer, or a faceless platform API. But your project and training data needs are unique. We can help.
Don’t just take our word for it. Here is what some of our retail AI clients say about CloudFactory:
We’re able to service large, multi-location enterprises because of our partnership with CloudFactory. We wouldn’t have been able to scale the company and deploy spatial intelligence without that help, and we wouldn’t be where we are now.
Zoë Cayetano
Head of Product and Chief of Staff, Pathr.ai™ Read the full case study
The CloudFactory team quickly caught on to what we were doing. They understood the eccentricities of the work and asked the right questions and acted very quickly on any feedback we had. Now it’s running like a well-oiled machine.
Gus Goldsack
Product Manager, Bizly Read the full case study
It’s hard for a company like ours to build and scale teams for large data annotation tasks. Especially because there can be significant churn in that workforce. People leave because the task is repetitive and it is hard to keep these teams motivated. It is much easier with CloudFactory.
Srivatsan Laxman
Founder and CEO, True Lark Read the full case study
We have been through a full production cycle of data sent through CloudFactory. We’ve fed that back into our model, trained it, deployed it and seen much, much better results and model accuracy.
Chief Technology Officer, Sensor-as-a-service company Read the full case study
CloudFactory does a really good job with quality. With the previous vendor, there were so many mistakes that we wondered whether to just throw it out and have it redone, which is ultimately what happened.
Data Quality Program Manager, leading cashierless checkout company
CloudFactory has been a reliable and robust partner for us as we scale our business. Their efforts have enabled us to quickly provide insights to our customers that wouldn't be possible without their help.
Matt Talbot
Co-Founder, GoSpotCheck
Proven performance in retail AI
CUSTOMER SUCCESS SPOTLIGHT:
CloudFactory delivers autonomous checkout
CloudFactory partnered with a leading AI retail company to implement shopping with autonomous checkout for brick and mortar businesses. The CloudFactory team exceeded targets for quality and throughput by labeling over 50,000 images per day, including keypoint annotations of human movement through retail and grocery stores to train an AI-Powered checkout product. CloudFactory also supported R&D experimentation for subjective keypoint annotations.
CUSTOMER SUCCESS SPOTLIGHT:
CloudFactory validation improves retail automation
A retail intelligence company that collects and analyzes online and in-store price data to drive business value for brands and retailers selected CloudFactory to verify software outputs against real-world data and validate store images taken by secret shoppers to enhance automation. The three-year partnership helped their product use a combination of data science and human validation to offer solutions for the retail industry.
CUSTOMER SUCCESS SPOTLIGHT:
CloudFactory helps power delivery service
CloudFactory was selected by a prepared food delivery service that relies on partnerships with restaurants for business expansion. The company needed manual annotation support to deduplicate data from a web scraping tool. The CloudFactory team cleansed restaurant data, including deduplication, ID assignment, and profile enrichment to train a machine learning model that identifies the accuracy of sales leads. We cleaned and enriched more than 13,000 restaurant profiles in just 30 days.
Recommended Retail AI Resources
- Blogs about data labeling and retail innovation (blog posts)
- 5 Qualities in Good Data Labeling Vendors (infographic)
- In-House vs Managed Workforce Data Labeling Partner (infographic)
- 3 Signs Data Labeling Provider Delivers Quality Data (infographic)
- Scaling Quality Training Data (white paper)
- The Outsourcers’ Guide to Quality (ebook)
- The Essential Guide to Computer Vision (ebook)
- Data Annotation Tools for Machine Learning (ebook)
- On-Demand Videos on Data Science and AI/ML (webinars)
Contact Sales
Fill out this form to speak to our team about how CloudFactory can help you reach your goals.
Retail AI - Frequently Asked Questions
When will robots replace retail workers?
We don’t envision a future where robots replace retail workers as we believe AI solutions should augment human potential. Humans have unparalleled cognitive abilities that make computers seem downright quaint in many situations. Robots help retail workers boost productivity, enjoy their jobs more, and free up time and energy to focus more on customer and employee engagement.
What role do CloudFactory’s clients play in annotating data?
Experts like you play a crucial role in helping us to formulate and understand images and videos in the initial data set during our analysis and seed processes. In the early stages of our work, we will partner closely with you to understand your requirements and determine how best to meet them. In most cases, we’re ready to go within two weeks. After that, how much your team wants to be involved is up to you. Some clients meet with our delivery teams weekly, others monthly. But of all the responsibilities involved in data annotation initiatives—from securing the facilities and workspace to hiring and firing, and from running payroll and securing technology to managing quality and providing ongoing training—you, as a CloudFactory client, play a role in just three: providing task guideline input and quality feedback and managing the initiative internally.
How should industry professionals and experts be incorporated into the computer vision annotation team?
CloudFactory teams are data annotation experts. At the start of each engagement, we work with you to understand business requirements and to train our analysts on your specific use cases and tasks. We’re familiar with many annotation tasks and use cases, and can quickly jump in to scale your annotation workload. We find that upfront communication about business requirements and as-needed, client-led training on complex tasks are keys to a successful computer vision annotation team’s success.
How do I prepare to work with an external team?
For retail image and video annotation, the first step is developing a detailed project scope and determining KPIs for quality, scalability, and project duration. At CloudFactory, a critical component in working with clients is having a dedicated project manager, who leads your analyst team, serves as your day-to-day contact, and optimizes your team’s outputs. We also provide a client success manager, who advocates for you, tracks outcomes to ensure we achieve target metrics, and troubleshoots as needed. These investments result in worker accountability, engagement, and a bias toward action—all of which contribute to better outcomes for your organization.
Does vendor experience matter?
Absolutely. Errors that lower data annotation accuracy result in poorly trained machine learning algorithms and the potential for high costs when deploying a model in a retail setting. Crowdsourced annotation providers often prioritize speed and task completion over training and accuracy which results in error-filled data that requires rework. A vendor with retail AI and computer vision experience also provides value by recommending annotation tools, techniques, and recommendations to optimize the entire AI lifecycle.
Should I use a managed team approach like CloudFactory, a crowdsourcing vendor, or hire in-house workers to train, validate, and optimize my retail AI models?
Typically, in-house employees can manage your data needs with reasonably good quality—until it’s time to scale your model. Contractors and freelancers are other options, but you need to train and manage them and control quality. It’s not easy, and costs can balloon. When you crowdsource, you use the cloud to send data tasks to many people at once. The problem with crowdsourcing is that compensation is usually based on speed, so quality suffers, and attrition is high. CloudFactory’s managed workforce model combines the expertise and quality of a trained, in-house team with the scalability of the crowd so you can get to market quickly with the highest quality annotations. Because annotators must meet or exceed strict quality standards, you get the same (or better) quality than you would from internal teams—without the burden of team management. Our model is ideal for data work because dedicated teams understand your business rules. They stick with projects long-term, enabling them to increase their throughput and accuracy while consistently providing high labeling quality. We also support the entire AI lifecycle, giving you the flexibility to modify the scope of projects as your needs change. This flexibility will help you control costs as projects scale, something that’s prohibitively expensive when scaling with in-house teams or the crowdsourcing model.
Do annotators need to be retail or robotics domain experts?
No, annotators don’t need to be retail professionals or have extensive retail experience. Your annotators will label your data effectively if properly trained on your project's data annotation techniques and business requirements. CloudFactory’s managed teams are accustomed to repeating the same tasks across similar use cases and industries, so they quickly increase the quality of annotations and the ability to scale while outperforming your in-house teams on labeling tasks. Our analysts pride themselves on their ability to learn their domains. Some of our annotation experts are also working in or studying highly technical fields from disciplines as diverse as mechanical engineering to biotechnology.
How can we speed the development of robotics data annotation projects without sacrificing quality?
At CloudFactory, our workforce delivers high-accuracy data annotations, iterates processes in real-time, and can quickly secure the domain knowledge required to resolve even the most challenging retail image edge cases. We can do this because we deliver tailored solutions that combine people, processes, and technology and have intricate knowledge of retail AI and robotics use cases, computer vision AI development, machine learning, and deep learning.
Can I replace in-house teams with external annotation teams and still maintain quality?
CloudFactory data annotation teams often exceed the quality of in-house teams while scaling projects faster. We work with some of the top computer vision retailers and have achieved 95.99% accuracy. The key is employing quality assurance methods that match the acceptable margin of error rates for each project and always putting quality first.
Does CloudFactory have the retail AI and computer vision experience they claim?
Demonstrating relevant experience is critical. CloudFactory has a growing list of past performances from more than 10 years of annotation experience and will provide additional references as needed. Learn more about our performance and partnership with retail AI clients.
Should we use automated (or AI-assisted) labeling for computer vision projects in retail?
We typically offer our clients a combination of both AI-assisted and manual, humans-in-the-loop data annotation—complementary styles for an experienced retail AI team like ours. Humans-in-the-loop annotation is critical for edge cases and exceptions, both those that raise accuracy flags and that ML models haven’t yet been trained to identify.
How do I improve my retail AI data quality and model performance?
At the start of every retail robotics project, establish quality targets. Falling below quality targets is generally related to a poorly trained algorithm and inaccurate data labeling. The key to improving quality at scale is using trained annotators experienced with automation and retail images.


